Polar bears live in marine environments where they swim and hunt seals for survival. But come to think of it, can they drown while swimming?
Yes, polar bears can drown although they are born swimmers. This happens when they are trapped in open water for a long time without access to ice or land.
In addition, when the sea pulls back, polar bears swim further and further out to sea in search of ice floes. Some spend all their energy doing so and end up drowning.
Now, we have learned that polar bears can also drown, but you might want to know how common this is. How many of them drown each year?
Continue reading to find out!
Table of Contents
- How Many Polar Bears Drown Each Year?
- Causes Of Drowning In Polar Bears
- How Long Can Polar Bears Swim?
- Can Polar Bears Breath Underwater?
- Can Polar Bears Drown As The Ice Shelf Melts?
- Recap
How Many Polar Bears Drown Each Year?
It is estimated that a small percentage, probably less than 1% of polar bears, drown each year.
Presently there’s no exact number of polar bears that drown each year. This is because polar bears live in remote areas and are difficult to study.
Some of them have been found dead in open water far from any ice.
A few cases of entire families drowning have also been reported. And this suggests they were overcome by tiredness or storms during a long swim.
Additionally, the risks of polar bears drowning are higher in certain areas like the Beaufort Sea in Alaska and northwestern Canada.
This is because the sea ice in these regions keeps moving backward. As the Arctic continues to warm, more polar bears are likely to drown.
This happens because these bears are forced to swim further to find sea ice platforms and hunt seals. This is a serious threat to the species’ survival.
Causes Of Drowning In Polar Bears
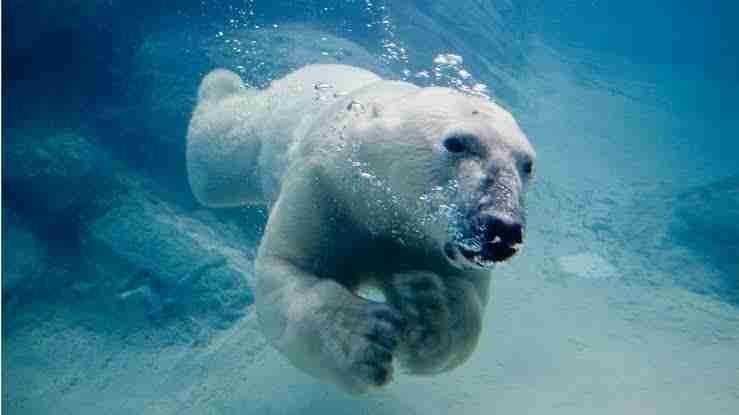

Here are a few reasons why polar bears can drown while swimming:
Exhaustion
Polar bears can swim long distances, but they get tired of swimming for extended periods. This happens especially in rough and frigid seas which can lead to exhaustion and drowning.
In addition, polar bear cubs are particularly at risk since they have less stamina. Exhaustion is more likely to happen if the bear has been starving or is in poor health.
Entrapment
On rare occasions, polar bears can become trapped under ice sheets or between ice floes, unable to surface for air.
As sea ice declines due to climate change, polar bears have fewer platforms to rest on. This now increases the risk of entrapment during long swims.
Entrapment can also happen near shore, where bears may swim into narrow inlets or passages they cannot come out of.
Lack of Experience
Young cubs just learning to swim are helpless to drowning, especially in unstable, icy waters. Polar bear cubs learn how to swim among many survival skills they learn from their mothers.
Sadly, orphaned cubs that have to fend for themselves at a young age don’t get this experience. So this affects their swimming abilities and puts them at higher risk of drowning in water.
How Long Can Polar Bears Swim?
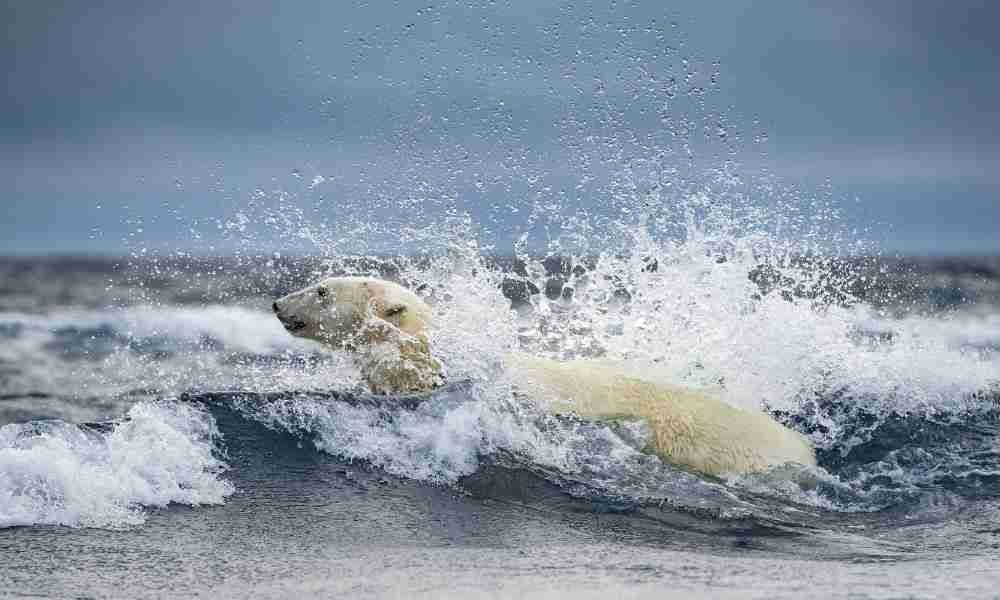

Polar bears can swim continuously for up to several hours at a time. Their large paws act as paddles and their fat body provides plenty of energy.
Additionally, the longest polar bear swimming session ever observed lasted for 232 straight hours (9.67 days). During this time, the bear (an adult female) covered 427 miles (687 km) in icy waters of about 2 – 6 degrees Celsius.
This was in the Beaufort Sea, north of Alaska and northern mainland Canada. Moreover, polar bears have been tracked swimming up to 100 miles non-stop but will eventually need to pull out onto land or ice flows to rest.
So while these polar bears have natural swimming abilities and can stay in the water for hours, they are not aquatic animals. They have limits.
Here’s a list of factors that can affect how long a polar bear can swim:
The Water Temperature
Polar bears are well covered by their thick fur and fat bodies. Nevertheless, they can get hypothermia (low body temperature) if they swim in icy Arctic waters for too long.
For this reason, they need to dry off and warm up on land.
Pregnancy/Nursing stage
Pregnant females and young cubs have less endurance and stamina for long-distance swimming. They typically stay closer to shore.
Polar Bear’s Size/Weight
Having enough food is a major factor in how long a polar bear can stay in the water. Polar bears are great swimmers and can cover long distances.
However, the length of time they can stay in water can depend on their energy levels. An adult male polar bear, which can weigh up to 1,500 pounds, needs a lot of food to keep going for long swims.
If a polar bear is hungry or hasn’t eaten in a while, they’ll have low energy reserves. So they’ll tire more quickly while swimming.
Can Polar Bears Breath Underwater?
No, polar bears cannot breathe underwater. However, they can stay underwater for about two to three minutes by holding their breath.
In fact, the longest polar bear dive that has ever been documented up till now lasted 3 minutes and 10 seconds. It covered a distance of 45 to 50 m (148-164ft ) without surfacing for air.
Interestingly, when traveling a great distance underwater, bears are known to hold their breath for no longer than two minutes. Although, polar bears sometimes stretch more than this duration.
As per research, polar bears can dive to a depth of about 20 feet (6 meters) in their natural habitat.
Can Polar Bears Drown As The Ice Shelf Melts?
Yes! Polar bears drown as the ice shelf melts. As the Arctic ice continually melts due to climate change, polar bears are losing their icy platforms.
They depend on these ice sheets for resting while swimming and hunting their prey. If they lose the icy platforms, it will lead to extended hours of swimming.
As a result, they lose their body heat and stored fat. This loss of heat eventually causes fatigue.
And when this happens, they might be unable to keep swimming, which can make them drown. Furthermore, some climate change models predict that polar bears could be nearly extinct by 2050.
This prediction is made based on the rate of polar bear drowning and the loss of sea ice in arctic regions.
Recap
In conclusion, polar bears can still drown even though they are excellent swimmers.
About 1% of them get drowned each year as a result of inexperience, exhaustion, and entrapment.
Interestingly, they have great swimming skills, which helps them last several days in water. Currently, the longest polar bear swimming session is 9.67 days.
In addition, their survival is tied to the melting and building up of Arctic sea ice. Hence, if the ice shelf melts, it increases the rate of drowning death for polar bears.
We concluded that polar bears can drown even when they are good swimmers like other bear species. But does this include giant pandas?
Can these bears swim despite being lazy and clumsy? Find out in our article ‘’Can Giant Pandas Swim?’’
Sources:
Two-thirds of the World’s Polar Bear Population at Risk of Extinction By 2050 – Biological Diversity
Research: Longest Recorded Underwater Dive By a Polar Bear