It is usually believed that bears have a good sense of smell but poor vision. Can this also mean that bears are blind?
Here’s the quick answer:
No, bears are not blind. The evidence suggests that bears and humans have similar visions.
In fact, bears are capable of excellent color vision. The rods and cones of their eyes are very much developed.
However, newborn bear cubs have no vision. They do not regain their vision until approximately 4 weeks.
So, now that we know that bears are not blind, let’s know about the eyesight of different bears.
Table of Contents
How Good Is A Bear’s Eyesight?
Bears have a vision that is similar to that of humans during the day.
However, bears, much like dogs or cats, have excellent night vision. Their vision is increased when they are in low light conditions.
This is due to the presence of the tapetum lucidum layer beneath their eyeballs. They are also able to detect motion very fast.
According to the ethnologist Harry Reynolds, bears have long-distance vision comparable to that of humans.
Black Bear
The eyes of black bears are brown in color and very tiny.
It is generally believed that black bears are capable of color vision. They also possess excellent near-point vision.
Recent studies have shown that their long-range vision is not very excellent. Also, they are unable to see huge objects. It is when the objects are viewed from a distance of more than 30 yards away.
RECOMMENDED READING: ARE BLACK BEARS COLOR BLIND?
Polar Bear
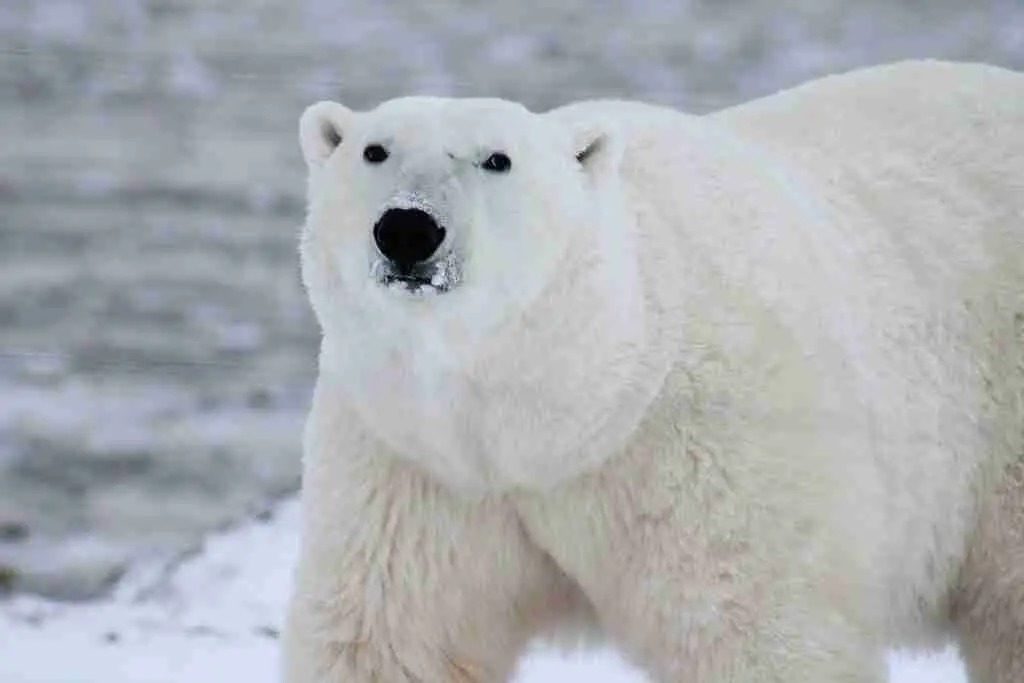

The eyes of a polar bear give good binocular vision as well as the ability to see on the bear’s flanks. The pupils are shaped like circles, and their eyes have a spherical shape.
The polar bear’s unique eyes are adapted to allow them to see better underwater.
When they are submerged, their eyes are protected by a transparent inner “eyelid”. This eyelid is known as a nictitating membrane.
This membrane also acts as a secondary lens for them to use. This trait is shared by many other marine animals. This membrane can also protect the eyes from the damaging effects of UV light.
It seems that polar bears and humans have a vision that is comparable to one another.
The vision length of polar bears is similar to humans. At the earth’s surface level, they can see up to the horizon, which is up to 5 kilometers away.
Grizzly Bear
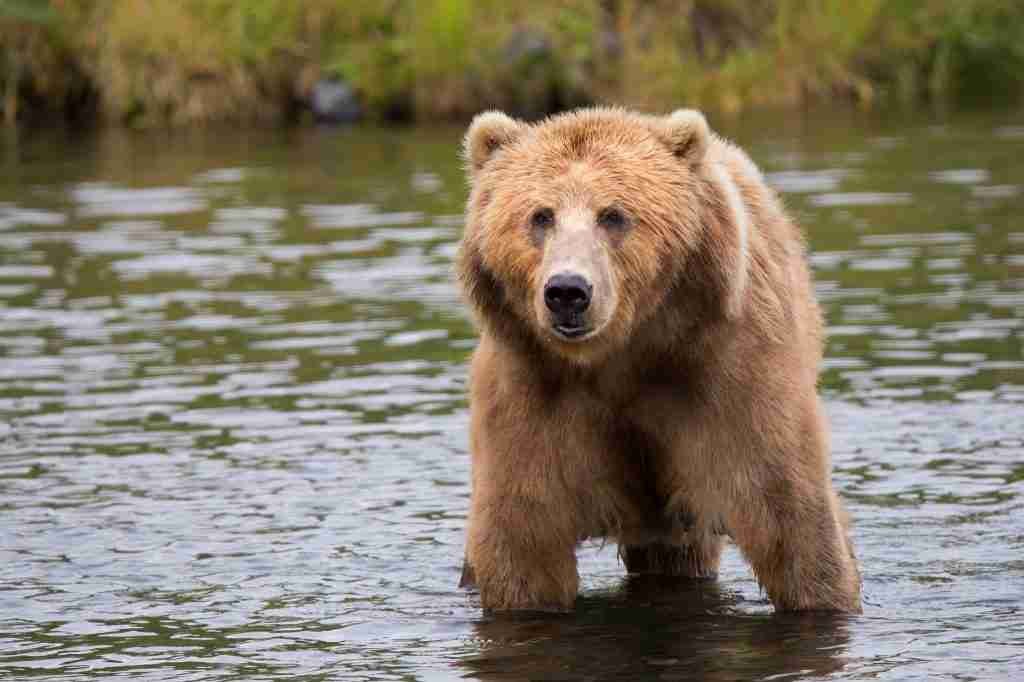

Grizzly bears or brown bears have quite good eyesight. They have eyes that are a brownish tint which absolutely goes with their body color.
They can see close things very clearly. But things in a long distance get blurry for them.
Although they are able to identify shapes even at certain distances, the details are not as clear. Grizzly bears are nonetheless able to identify objects at a distance of up to 61 meters.
However, similar to other bear species they have the ability to see in the dark.
Sun Bears
Sun bears have comparatively poorer eyesight than other bear species.
Because of their poor eyesight, sun bears must rely on their keen sense of smell to locate food.
In addition, the sun bear’s eyes are set in a more forward-facing position than polar bears. Polar bears have longer nose areas. This is another adaptation that is believed to assist the sun bear in climbing.
However, sun bears have beautiful blue eyes which are very different compared to those of other bears.
Panda bear (Giant Panda)
The panda bears, like many other nocturnal species, possess outstanding night vision. Thanks to its pupils, which are shaped like vertical slits like cats. Whereas every other species of bear has a circular pupil.
However, their far vision is blurry and they also cannot see many colors. They can see no further than approximately five feet in front of them.
Rods are more numerous than cones in the eye of the giant panda. As a result, have sharp night vision.
RECOMMEND READING: ARE GIANT PANDAS COLOR BLIND?
Sloth Bear
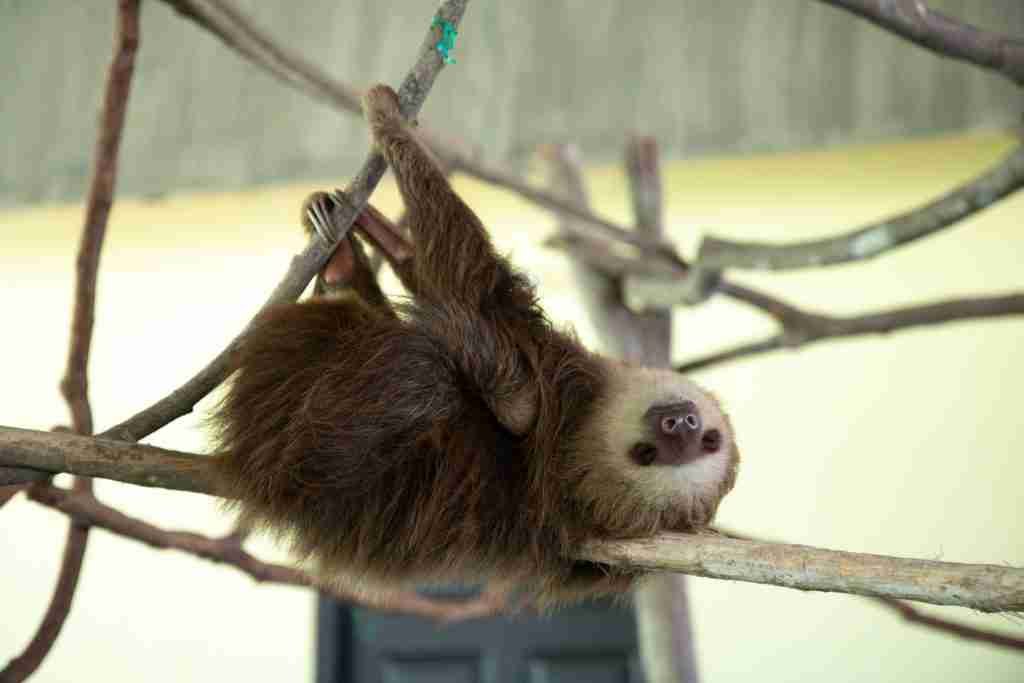

The sloth bear’s vision is not that good compared to other bears. They have round brown colored pupils.
Due to poor eyesight, they feel threatened whenever something unusual happens. And they get aggressive to defend themselves.
Both near and far eyesights are problematic for sloth bears.
What Color Can Bears See?
The one cone is sensitive to light with short wavelengths, allowing bears to see blue-violet light. The second cone is sensitive to light with long wavelengths, allowing it to see a yellow light.
Bears, in particular, have excellent color vision, particularly toward the blue portion of the spectrum.
Although they can’t see reds as effectively as we can, their vision is undoubtedly greater than that of deer.
This can be examined from the number of rods and cones present in their eyes as well as their positions. Cones are responsible for color perception, while rods gather light.
A study was done at the University of Tennessee by Ellis Bacon and Gordon Burghardt. According to that research, black bears are able to distinguish between different tints of color.
In this experiment, bears were first trained to link different colors with different foods.
After that, the bears were given the same container with different colors. The “blue-trained” bear was able to correctly differentiate between blue, blue-gray, blue-green, blue-red, and blue-yellow.
The “green-trained” bear was able to differentiate between green and related colors.
The American black bear appears to have more sensitivity to wavelengths of blue and green light. It’s possible that they’re even sensitive to the color red.
It is likely that the ability to perceive colors helps them in finding food. It is because most of their foods include various colored berries and fruits.
Furthermore, compared to beige tents, the yellow-and-blue tents attract the bears more.
Do Bears Have Night Vision?
There is some truth to the notion that bears possess night vision. Bears have a tapetum lucidum located in the back portion of their eyeballs. This is common to many nocturnal species.
This is a layer of reflecting tissue. This layer is responsible for increasing a bear’s night vision. It reflects light back through the retina.
It also enables light to trigger light-sensitive cells within the retina for a second time. This is essential for good night vision and sensitivity to any movement in the night.
Compared to humans, polar bears have excellent night vision. Their eyes include a greater amount of photoreceptor cells in the retina.
This helps them to see in low light. The polar bear’s good night vision is important for their survival, especially during winter. This is because during winter the nights are longer than the days.
Recap
Bears have excellent eyesight. They can see pretty well even at night. Moreover, they are able to see in different colors.
So much research has been done particularly on their eyes. And it can be easily said that the eyes of bears are similar to human beings, cats, and dogs.
Moreover, bears have different types of eyesight. While some are nearsighted, some can see up to very far. But more or less, all types of bear species can see very well.
In fact, you might have heard that pandas are color-blind. Is it true? Find out the truth here!